How is Cardiac Arrest differ from Heart Attack? Know its sign, causes, and treatment

If you think heart attack and cardiac arrest are same, you are not alone. These two terms have a vast difference in their actual meaning.
Heart attack, stroke and cardiac arrest are familiar terms. Many people assume that heart attack and cardiac arrest are the similar attacks but with different names, however, in reality, they are very different from each other.
As per a report of AHA 2015, the average survival rate of cardiac arrest is 10.6%. It accounts for more than 350,000 deaths each year only in the United States itself.
Major Difference Between Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack
Sudden Cardiac Arrest occurs when the heart malfunctions. It stops beating at a sudden without any warning signals.
If the condition happens, blood stop flowing to several vital organs including brain, lungs, and kidney. After some seconds the victim loses consciousness. Death is certain if the heartbeat is not restored with an electrical shock.
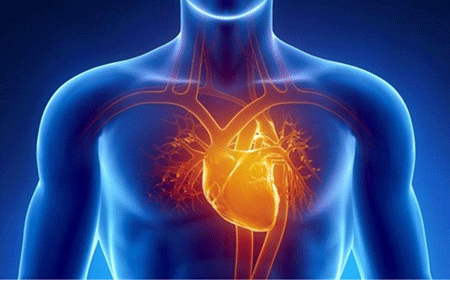
In contrast, the heart attack is a condition when a blocked artery prevents oxygen-rich blood reaching a section of the heart.
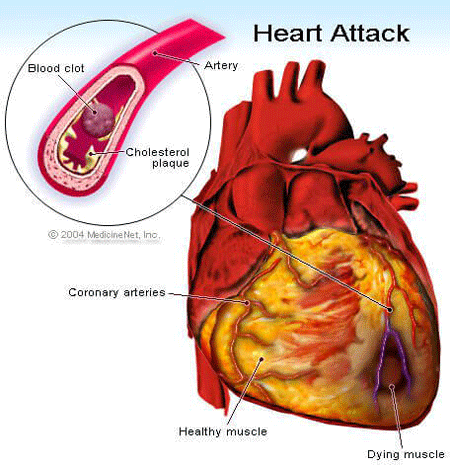
The heart muscle is deprived of its vital blood supply and if not treated in time the part of the heart begins to die.
Signs and Symptoms of Cardiac Arrest
- No pulse
- Breathing problem
- Unconsciousness
- Turning Bluish in color
- Eyes rolling back into head
Symptoms of Heart Attack
There are some clear and notable differences in symptoms of heart attack and cardiac arrest.
Some of the signs spotted in a patient suffering from the heart attack are:
- Sudden pain and discomfort in upper abdomen including chest, arms, or jaw
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath; sometimes problem in breathing may occur
- Unusual level of fatigue
- Cold sweat
- Nausea, vomiting, and indigestion
- Tightness in chest, neck, and arm.
Causes of Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack
In most cases, cardiac arrest is followed by an abnormal heart rhythm called ventricular fibrillation. VF is the state where the electrical activity of the heart is disrupted.
VF can be caused by following factors:
- Coronary heart disease
- Heart attack
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart disease
- Heart valve disease
- Acute Myocarditis
Prior heart disease is a major risk factor encountered in patients. Additionally, a family history of cardiac arrest in a first-degree relative is often the case with 2 fold increase in the risk of cardiac arrest.
Well, in contrast to cardiac arrests, the heart attack is generally caused by Coronary heart disease (CHD) with some of the risks associated with it.
Some of the risk factors are listed below:
- Smokers
- Unhealthy diet; heavy consumption of saturated fat
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- People who do not perform some daily exercises.
- People exposed to an excess of air pollution, particularly the traffic pollution.
Treatment and Preventive Measures
Treatment is basically associated with some procedures to open up the blocked blood vessel and restore blood supply to the heart.

The risk of the heart attack an cardiac arrest can, however, be prevented and reduced to a remarkable level changing some daily lifestyle.
Performing physical exercise in regular basis can be a beneficial step. Quitting smoking is the single best thing that can be done to improve health status.
The preventive measures help to avoid possible heart issues including some forms of cancers as well.
For more updates and health-related articles visit our official page.
