What is Cleidocranial Dysostosis? The Rare Disorder That Affects Your Bones and Teeth; Learn Its Symptoms, Effects, and Treatments
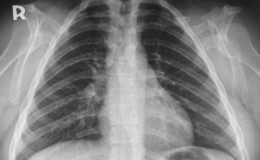
Cleidocranial Dysostosis is a condition that generally affects the development of bones and teeth. It is also known as Cleidocranial dysplasia (CDD).
Cleidocranial Dysostosis is a condition that generally affects the development of bones and teeth. It is also known as Cleidocranial dysplasia (CDD).
In such condition, the collarbones are either poorly developed or totally absent, that allows the victim to bring their shoulders closer together. The prevalence of CDD is 1 per million people in the world.
Intelligence in a victim is typically normal but the symptoms of this disorder vary from person to person.
What is Cleidocranial Dysostosis?
The term ' Cleidocranial Dysostosis' comes from the words cleido (collarbone), cranial (head), and dysostosis (abnormal bone formation).
CDD is often characterized by the delayed maturation of the skull including the delayed closing of the growth lines where bones of the skull meet.
Causes:
The condition is either inherited from parents or sometimes as a result of new mutation. It is caused by changes in the PUNX2 gene and inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
It is a congenital condition, which means it is present in a victim before birth. CDD is not biased of gender as it affects both male and female equally.
Signs and Symptoms
As stated above, the signs and symptoms of cleidocranial dysostosis vary widely even in the same family itself.
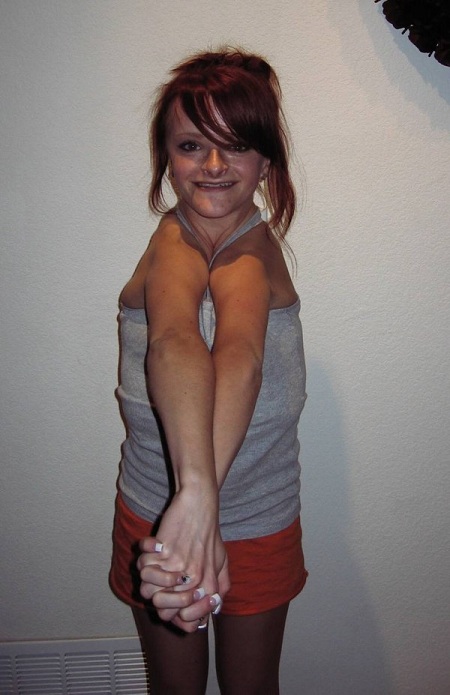
There's either the complete absence of collar bone or its abnormally developed. Adult teeth may develop later than normal.
Individuals with cleidocranial dysplasia often have decreased bone density (osteopenia) and may develop osteoporosis.

Dental abnormalities are very common in the victims and can include delayed loss of the primary teeth, delayed loss of secondary teeth and sometimes unusually shaped.
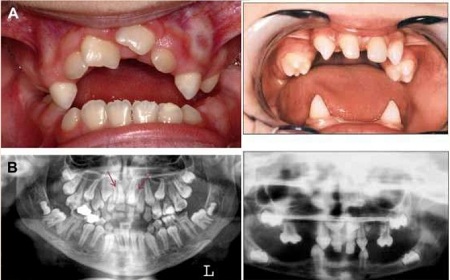
In addition to dental and skeletal abnormalities, people may also have a hearing impairment; may also be prone to sinus.
Symptoms generally include:
- Ability to touch shoulders together in front of the body
- Prominent forehead (frontal bossing)
- Delayed closure of fontanelles ('soft spots')
- Short forearms
- Short fingers
Characteristic Facial Features include:
- A wide, short skull
- A prominent forehead
- Wide-set eyes (hypertelorism)
- Flat nose
- Small upper jaw
Diagnosis and Treatment
Cleidocranial dysostosis is diagnosed with a physical examination and X-rays of different body parts including head, chest, and hands.
To confirm CDD, a genetic testing of the RUNX2 can also be considered. People suffering from the condition may undergo a different type of genetic testing called chromosomal microarray (CMA).
A fetus can also be tested during pregnancy. It can be tested by obtaining its cells through chorionic villus sampling in the first trimester or amniocentesis in the second trimester.
Though CDD has no specific treatment, the condition can be managed based on each symptom detected.
Most of the victim require dental care due to dental abnormalities. If a victim has low bone density, Vitamin D, and Calcium supplements are recommended.

Those with some kind of ear defect may require ear tubes; victims are recommended to wear a helmet during high-risk tasks.
Surgical procedures may be performed to fix certain bone abnormalities.
Here's a video of young actor Gaten Matarazzo sharing his rare condition of cleidocranial dysplasia on The Doctors Show.
All in all, the disorder prevails throughout a person's life and most consider it as a taboo for which public awareness is needed.
Prevention
Genetic counseling plays a key role if a person with a family or the person himself is planning to have kids.
The symptoms of cleidocranial dysostosis cause only a few manageable problems. Hence, for comfortable living, appropriate medical care is very essential.
